The ICAN IHU MASH (NASH) Clinic
An innovative care pathway unique in France
The MASH (formerly NASH) clinic was set up in 2019 by a multidisciplinary team from the AP-HP, with the support of the ICAN IHU. Its aim is to optimise the diagnosis and management of people suffering from hepatic steatosis, to improve control of their disease and to slow, or even halt, its progression towards serious forms (cirrhosis, liver cancer) requiring major operations such as liver transplants.
What is MASH?
MASH (Non-Alcoholic Hepatic Steatosis), formerly known as NASH, is a liver disease caused by an accumulation of fat of metabolic origin independent of alcohol consumption or viral hepatitis. It is very often the consequence of an excessively sedentary lifestyle combined with a diet too rich in fats and sugars. The risk is a progression to serious diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
In France, 18% of the general adult population are affected. People with MASH are often asymptomatic, and are at greater risk of developing cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. Conversely, these co-morbidities, particularly obesity and diabetes, are risk factors for the progression of liver damage to the most severe forms (cirrhosis and liver cancer). The multiplicity of pathologies associated with MASH all too often leads to a fragmentation of medical care, with no coordination between the many people involved.
Improving diagnosis among the many people at risk so that care can be taken earlier to avoid progression of the disease and the development of other pathologies is a public health issue. There is also an economic challenge, as the cost of treating this disease weighs heavily on the social security budget.
Teams from the AP-HP and the ICAN IHU have therefore set up the MASH clinic to offer patients an innovative, multidisciplinary and personalised care pathway.
The mission of the MASH clinic
The MASH clinic is the first hospital-based facility for the diagnosis and multidisciplinary management of patients suffering from metabolic steatosis in France.
More than 350 patients have already benefited from its services. The aims of the MASH clinic :
- To offer personalised care to each patient, taking into account their clinical phenotype, personal history and environment, to ensure the best possible compliance with medical recommendations.
- Anticipating and intercepting the complications of MASH (early atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, diabetes, etc.).

The ICAN IHU has made available dedicated human resources (1 doctor and 1 nurse) as well as its clinical investigation centre, and has provided the conditions needed to build this pathway thanks to its cross-disciplinary and multidisciplinary approach to cardiometabolic and nutritional diseases.
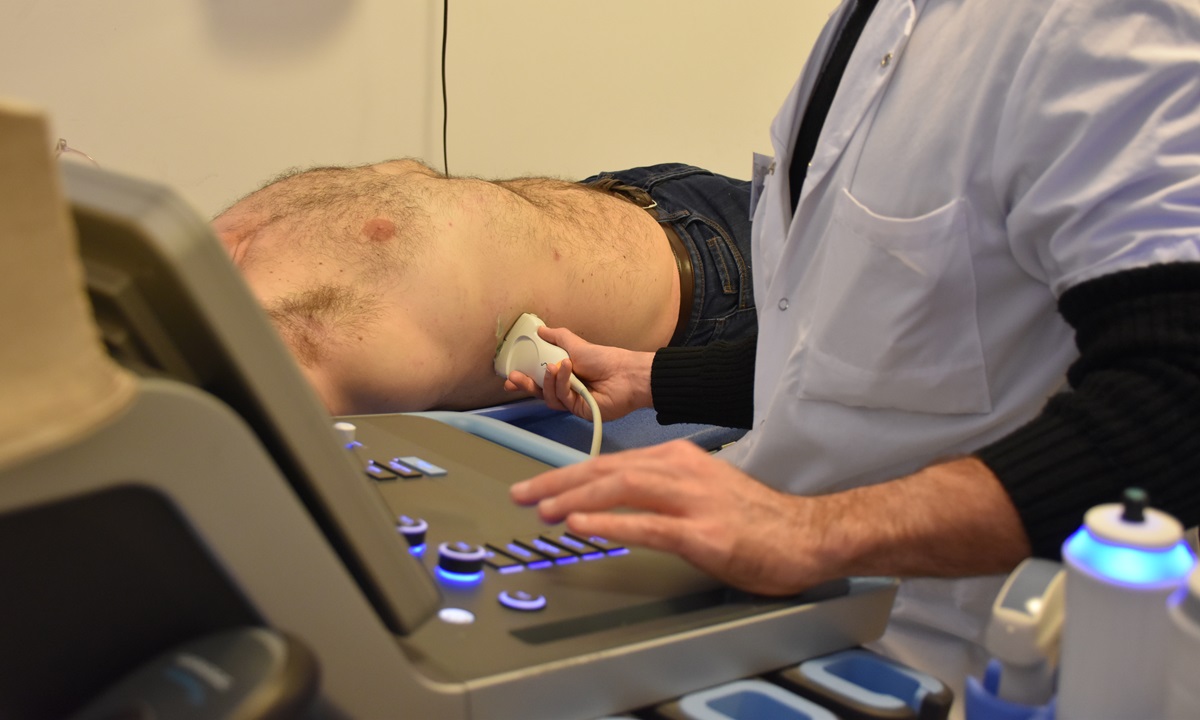
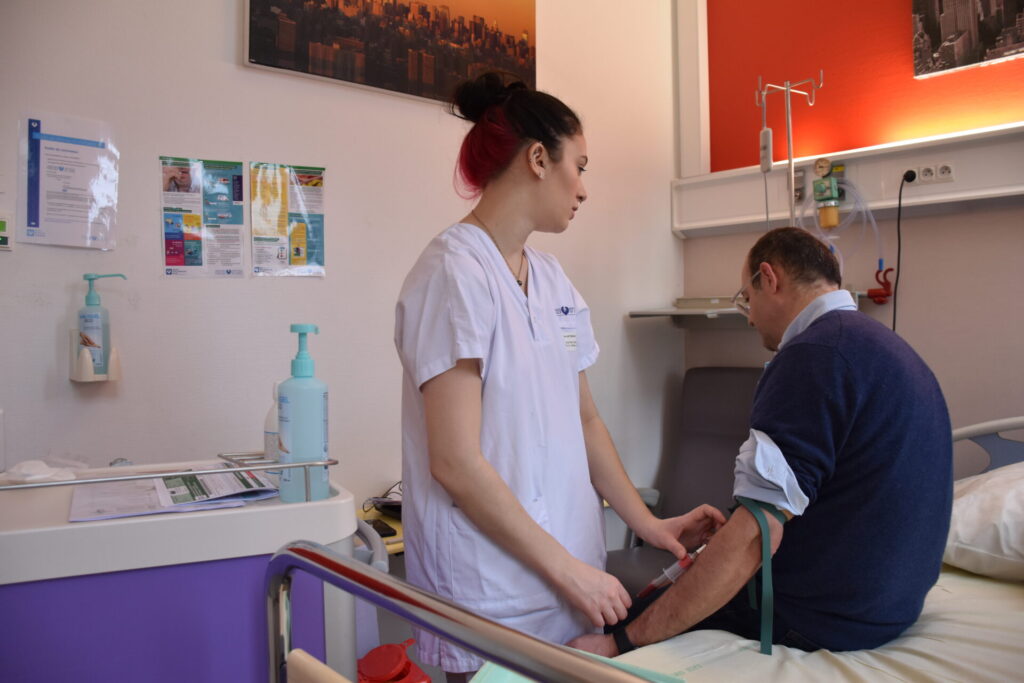
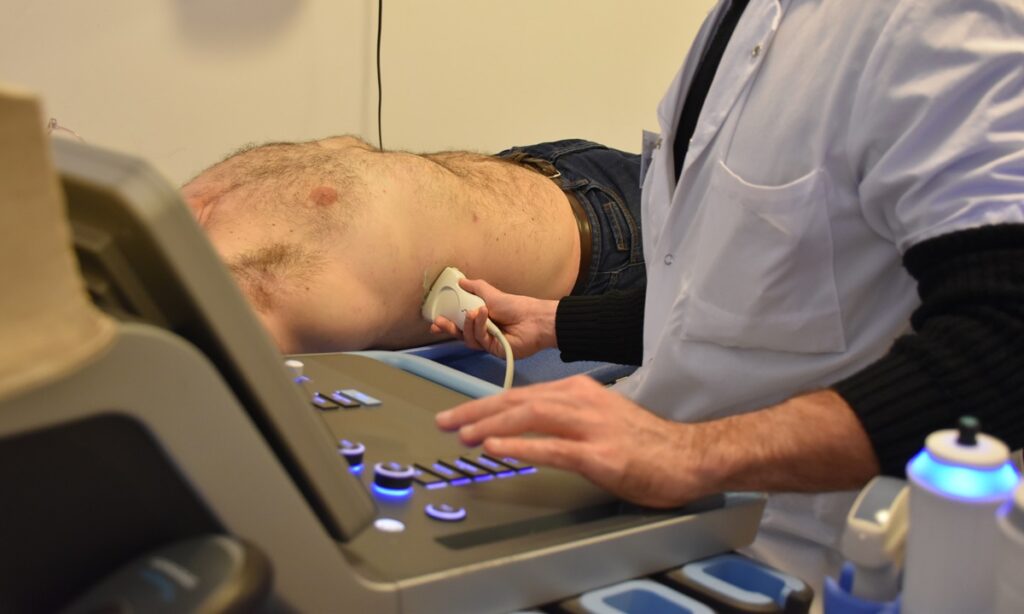
The patient pathway is simplified and unified as part of a day hospitalisation in the hepato-gastroenterology and nutrition departments of the Pitié-Salpêtrière hospital.
Various medical specialists (hepatologist, radiologist, cardiologist, dietician, diabetologist, surgeon, etc.) are mobilised to carry out the examinations needed to establish a phenotype and a precise diagnosis, with an assessment of the hepatic and cardiometabolic risk. To provide better support for patients, the circuit also offers a therapeutic education consultation, which is essential if patients are to adhere more effectively to the therapeutic programmes on offer.
The strengths of the MASH clinic
- Multidisciplinary, cross-disciplinary approach
- Unified, fluid circuit
- Personalised care
- Dedicated human resources
- Integrated care and research

Dr Raluca Pais
Hepatologist/Gastroenterologist – Lead doctor at the MASH clinic
” Patients undergo all the tests required to diagnose their condition and assess their personal risk of progressing to more serious forms or developing other pathologies in a single day : liver tests to assess the severity of liver damage; cardiovascular tests – coronary calcium score to identify early atherosclerosis lesions; metabolic tests to assess the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and metabolic co-morbidities

Prof. Vlad Ratziu
Hepatologist/Gastroenterologist
“To counter the development of MASH in the French population and reduce the number of hospital admissions due to MASH, it is essential that patients understand the risk of their disease developing and the associated co-morbidities, so that they can make lasting changes to their lifestyle